This is an old revision of the document!
Network-related FAQs
Wake-on-LAN
What is WOL?
Wake-On-LAN (WOL) is a standard procedure to wake up a computer over a network. A special broadcast frame called “Magic Packet” is sent to the network adapter that triggers the startup process.
Which Shuttle models support WOL?
WOL (Wake-on-LAN) is supported by all Shuttle devices by default.

How do I activate WOL?
Please start your Shuttle XPC and press the [DEL] or [F2] key while booting to enter BIOS.
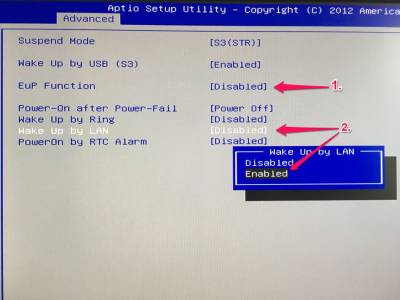
- Navigate to tab “Advanced”
- Please deativate the EuP function.(1)
- Now activate Wake Up by LAN (2)
- To save, please press
F4on your keyboard.
Which states can a Shuttle XPC be woken up from?
A Shuttle XPC supports the following states:
- S3 (Suspend-to-RAM – STR)
- S4 (Suspend-to-Disk – STD)
- S5 (Soft-Off)
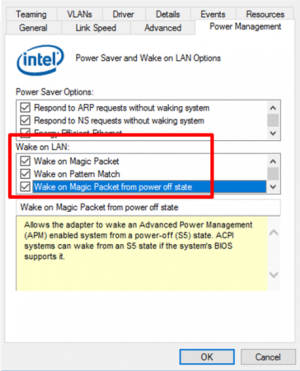
Which drivers must be installed?
Please use the network card driver provided by Shuttle. This driver is already preset for WOL use and requires no further settings.
If you happen to run other drivers, please go to “Device Manager → Network Adapter → Properties” to activate WOL for Magic Packet.

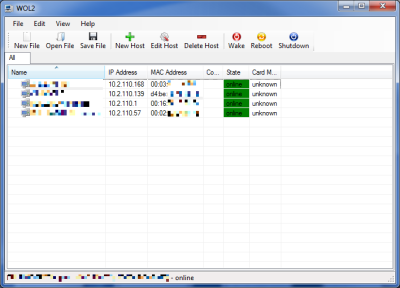
How do I wake up a Shuttle XPC under Windows?
We therefore recommend the popular freeware tool “WakeonLan2” (WOL2) with support for Windows and Linux.
| Tool | Download |
|---|---|
| WakeOnLan Tool 2 | https://oette.wordpress.com/wol2/ |
How do I wake up a Shuttle XPC under Linux?
Firstly, please bootup the Shuttle XPC and active WOL in BIOS.
WOL must also be activated under Debian/Ubuntu.
Please use the following command: ethtool -s eth0 wol g
The etherwake command can be used to send a Wake-On-LAN “Magic Packet” under Linux operating systems.
Please enter the following command to install etherwake under Debian/Ubuntu Linux desktop: $ sudo aptitude install etherwake
Note: Red Hat Linux users should use the net-tools package which is installed by default.
To initiate the wake up process, please type the following command using the appropriate MAC-Address: # wakeonlan MAC-Address-Here